Basic Endgame Principles !!!!
Endgame is something that can bring their chess to the next level. Because endgame involves far fewer pieces than opening or middlegame, it is a phase of the game that can be mastered by a player of pretty much any skill level.
Endgame Principle 1. Centralize your king as soon as possible!
This is by far the most fundamental endgame rule. Surprisingly many amateurs neglect this important principle often missing a big opportunity to win or draw the game. The idea of centralizing the king is rather simple. In the endgame, when the majority of the pieces are gone, the king becomes a powerful weapon and should actively participate in the game to support his own pawns and piece as well as to attack the opponent’s ones.
The first step of your thinking in any endgame position should be how to centralize your king quickly and efficiently.
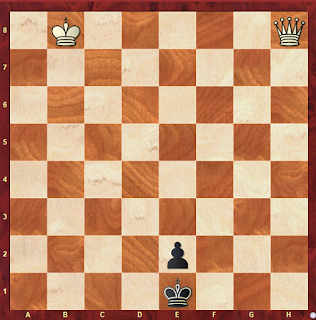
In the position below white has a serious advantage because they centralized king three moves earlier than black.
 |
| Black to Move |
Endgame Principle 2. When you up in pawns exchange the pieces
This is a pretty straightforward rule to understand. If you up a pawn, with pieces on the board the position may still be ambiguous. However, if you simplify the position further by taking pieces off the board, the extra pawn will immediately play a greater role and can even decide an outcome of the game.
In the position below white is up a pawn. That’s why it is a good idea for them to trade the minor pieces. By forcing that exchange white will be able to easily take advantage of the extra pawn, winning the game.
 |
| Black to move |
You should be very careful about exchanging pawns in positions like shown above. In the extreme situation, after exchanging all of the pawns you will end up in a Knight + Pawn vs. Knight endgame which may easily end in a draw because black will simply give up his knight for a pawn. To avoid this scenario, if you up some pawns, exchange pieces, not the pawns.
Endgame Principle 3. Obtain an opposition
The opposition is a powerful endgame technique. It is commonly used to force the opponent’s king away from the pawns, giving up control of the key squares. Generally, a side that holds an opposition has a positional advantage, often winning or drawing the game.
The position below is the most classical example of the opposition. If it is white’s turn to move the game is drawn because white cannot penetrate black’s position without advancing the pawn. If it is black’s turn to move, black needs to give up space and loses. In other words, the side that holds an opposition has some sort of advantage which is enough to win or save the game. (for more Clear vision few our earlier blog).
 |
| White to play |
Endgame Principle 4. Flank pawns are strong against the knights
Endgame Principle 5. Place the rook behind the passed pawn
This is another very important rule to remember. Many amateur players disregard this simple rule placing the rook in front of the passed pawn and then have trouble converting the advantage.
Don’t make that mistake and always remember to place the rook behind the passed pawn. This placement of the rook supports the pawn all the way through the promotion square and also makes it possible to threaten the opponent’s king or pawns from the safe distance.
You should also keep this rule in mind when you’re attacking opponent’s passed pawns. By placing your rook behind the opponent’s passer, you control the pawn all the way through the promotion square making it much harder to defend.
In the position below white has placed his rook behind the passed pawn and supports it all the way to the promotion square.
 |
| Black to Play |
Endgame Principle 6. Create a passed pawn
Creating a passed pawn should be one of the priorities in the endgame. Passed pawn possesses a large value due to the possibility of promotion. In fact, a passed pawn is so valuable that if it reaches the 7th rank it is worth a rook.
It is especially easy to create a passed pawn if you have a pawn majority on one side of the board. In the example below, white can easily create a passed pawn by first exchanging the b-pawn on the opponent’s c-pawn and then exchanging off the opponent’s b-pawn.
 |
| Black to Play |
Endgame Principle 7. If you are exchange down avoid trading rooks
If you have a minor piece for a rook (aka exchange down) you should save the remaining rook, since this is the only piece that can guard open files and ranks. Without this piece, your position will collapse and the pawns will fall.
In the position below black is exchange down. White offers a rook trade, but black wisely rejects it attacking white’s weakness the backward b-pawn. With the correct play, black has a good chance to draw this position.
 |
| White to Play |
Important Points: The endgame is no doubt a very important part of chess. If you want to improve your chess level, you need to have a clear study plan. If you aim for a dramatic improvement at chess you need to work on all of the elements of the game in a systematic way:
- tactics
- positional play
- attacking skills
- endgame technique
- classical games analysis
- psychological preparation
- and much more



Comments
Post a Comment